
India reports first case of monkeypox
India has reported its first confirmed case of monkeypox after a 35-year-old man with a history of travel to the Middle East showed symptoms, officials said.
The federal government rushed a multi-disciplinary team to the southern state of Kerala in view of the confirmed case of monkeypox there, according to an official statement.
The man, who travelled from the United Arab Emirates to Kerala on Tuesday, was in stable condition and isolated at a hospital, the state's health minister Veena George told reporters Thursday.
"He is stable and all his vital signs are normal. We have asked all districts to be on alert," she said.
The patient's primary contacts have also been isolated while passengers who came in contact with him on his flight have been told to monitor themselves for symptoms.
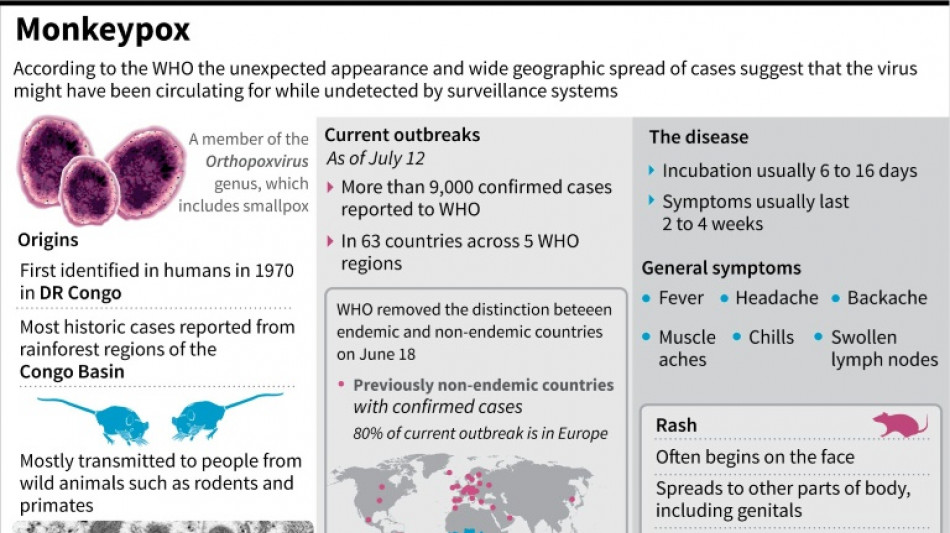
Monkeypox is an infectious disease caused by a virus transmitted to humans by infected animals. Human-to-human transmission is possible but considered rare.
A surge in monkeypox infections has been reported since early May outside the West and Central African countries where the disease has long been endemic.
So far, confirmed cases in non-endemic areas are generally mild and no deaths have been reported.
It is considered much less dangerous and contagious than smallpox, which was eradicated more than 40 years ago.
The first symptoms of monkeypox are a fever above 38.5 degrees Celsius, headaches, muscle pain and back pain during the course of five days.
Rashes subsequently appear on the face, the palms of hands and soles of feet, followed by lesions, spots and finally scabs.
Transmission comes through close and prolonged contact between two people, principally via saliva or the pus of scabs formed during infection.
Most monkeypox infections so far have been observed in men who have sex with men, of young age and chiefly in urban areas, according to the WHO.
The disease has a fatality rate of between one and 10 percent depending on the variant -- there are two -- in endemic countries.
But medical care significantly reduces the risk. Most people recover on their own and outbreaks usually die out on their own due to low transmissibility of the virus.
P.MacNair--NG